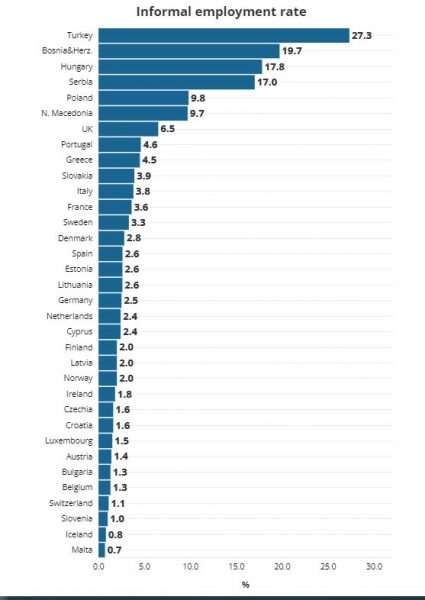
According to a recent report by the UN International Labour Organization (ILO), Greece is now the second-highest country in the Eurozone for informal employment, trailing only behind Portugal.
The report equates informal employment with “zero-hour contracts,” where workers are employed whenever and for however long the employer desires. This type of employment is often characterized by a lack of legal protection, social security, and formal contracts.
The ILO estimates that in 2023, around 58% of the global workforce was engaged in this type employment, dropping to 50% when excluding agricultural workers. In Europe and Central Asia, informal employment recently affected 1 in 5 workers.
Hungary and Poland had the highest rates of informal employment among EU countries, with 17.8% and 9.8%, respectively. In contrast, the informal economy is much less prevalent in other member states falling below 2% in one-third of the EU countries.
Informal employment in Greece reaches nearly double the rate seen in other Eurozone countries.
Reports from ERGANI, the digital platform of the Hellenic Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs, estimated undeclared work in Greece at around 5% in 2020, a significant drop from the 40% observed during the peak of the economic crisis in 2013.
However, experts like Ioannis Kouzis, Professor of Labor Relations at Panteion University, argue that these figures are likely underestimations. He suggests that true levels of undeclared work are much higher, considering that many cases go undetected by labor inspections.
Furthermore, Greece has seen the introduction of “on-demand work” contracts, a variation of zero-hour contracts, further complicating the landscape of such employment. These contracts, introduced by recent legislation, allow employers to call employees for work as needed, with minimal guaranteed hours, further blurring the lines between informal and formal employment.