An IMF report released this week predicts that Greece’s public debt will be cut by 30 percentage points by 2029, with the Washington D.C.-based Fund also predicting that Italy, by that year, will have assumed the unenvious title of highest GDP-to-debt ratio among European countries – but with the former remaining in second place.
The consistently decreasing GDP-to-debt ratio is due to economic growth, inflation and a 2018 agreement between the coalition Greek government at the time and institutional creditors, mainly the ECB and Eurozone partners. The agreement extends to 2032 and includes so-called “interim measures” agreement between Greece and its creditors to reduce the public debt. The period after 2032, however, remains a question mark.
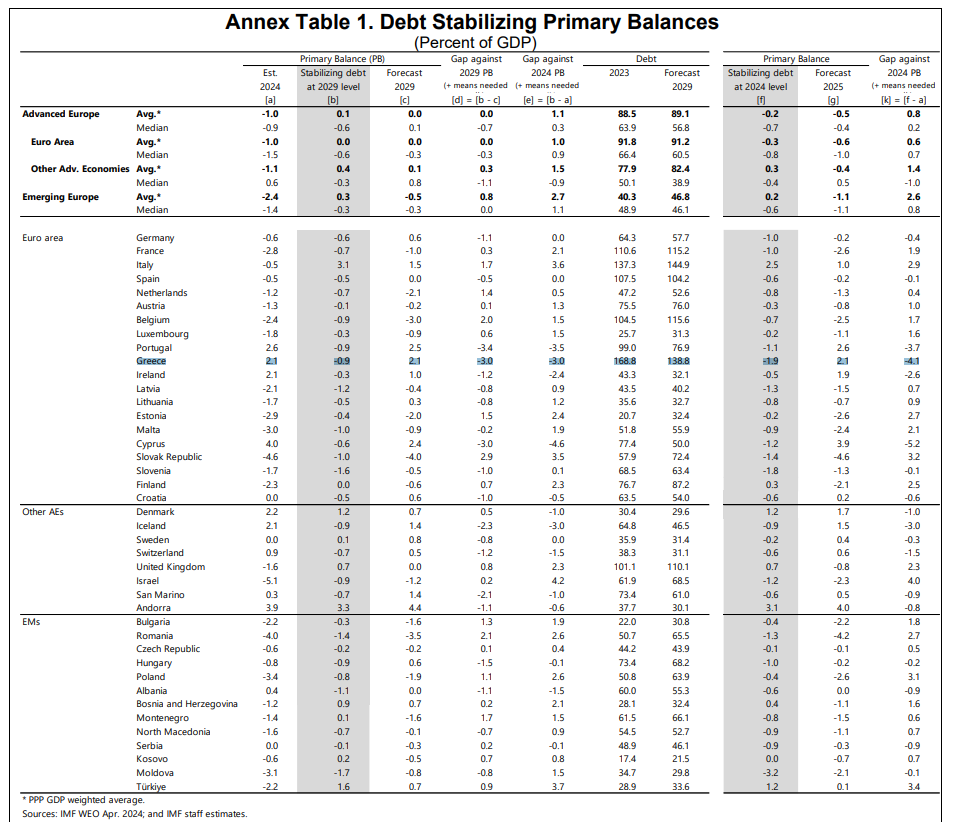
Specifically, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts that the GDP-to-debt ratio will drop to 168.8% by 2029, down from 138.8% in 2023. The forecast is included in the IMF report on Europe, entitled “Taming Public Debt in Europe: Outlook, Challenges, and Policy Response”.
Conversely, the IMF forecast for Italy has the same ratio for that country climbing to 144.9% in 2029, up from 137.3 in 2023.
The “calculus” for Greece, among others, is based on a forecast of a 2.1% primary budget surplus this year and in 2029. The latter is accompanied by forecasts for continued economic growth and inflation.


